Advanced Sensor Noise Reduction in UV Visual Systems
UV visual systems have become a critical component across multiple industries, including industrial printing, quality inspection, electronics manufacturing, medical diagnostics, and scientific research. These systems rely on highly sensitive imaging sensors to capture ultraviolet light with precision and consistency. However, one of the most persistent technical challenges affecting performance is sensor noise. Noise degrades image clarity, reduces measurement accuracy, and can compromise automated decision-making processes.
As UV imaging applications demand higher resolution, faster speeds, and improved reliability, effective sensor noise reduction has become a core design and optimization priority. Noise is not a single problem but a combination of physical, electronic, and computational factors that must be addressed holistically. Modern UV visual systems therefore integrate advanced hardware design, signal processing algorithms, calibration workflows, and intelligent software techniques to minimize noise without sacrificing detail.
This article provides an in-depth, practical, and up-to-date exploration of sensor noise reduction techniques in UV visual systems. It explains noise sources, analyzes reduction strategies, discusses real-world implementation challenges, and highlights future trends shaping next-generation UV imaging solutions.
Understanding Sensor Noise in UV Imaging

Sensor noise refers to unwanted variations in pixel values that do not represent actual light information from the target scene. In UV visual systems, noise is often more pronounced than in visible-light imaging due to lower photon counts, higher sensor sensitivity requirements, and stricter accuracy demands.
Unlike visible imaging, UV systems frequently operate in low-signal environments where even small noise fluctuations can overwhelm meaningful data. Noise may appear as graininess, random speckles, fixed patterns, or subtle distortions that interfere with edge detection, color consistency, alignment accuracy, and defect recognition.
Understanding the fundamental nature of sensor noise is essential before selecting appropriate reduction techniques. Each noise type has distinct characteristics and requires targeted mitigation strategies.
Major Types of Sensor Noise in UV Visual Systems
Thermal Noise
Thermal noise is caused by the random motion of electrons inside sensor circuitry. This movement occurs even when no light is present and increases as temperature rises. In UV sensors, thermal noise can be particularly problematic because exposure times are often longer to compensate for lower UV light intensity.
Thermal noise manifests as random pixel fluctuations across the image and is difficult to eliminate entirely. However, it can be significantly reduced through temperature control, optimized sensor materials, and advanced signal processing.
Shot Noise
Shot noise originates from the discrete, particle-based nature of photons and electrons. In low-light UV environments, the statistical variation in photon arrival rates becomes more noticeable, introducing randomness into the captured signal.
Unlike other noise types, shot noise cannot be fully removed because it is a fundamental physical limitation. The only way to reduce its impact is to increase signal strength, improve quantum efficiency, or apply intelligent averaging techniques.
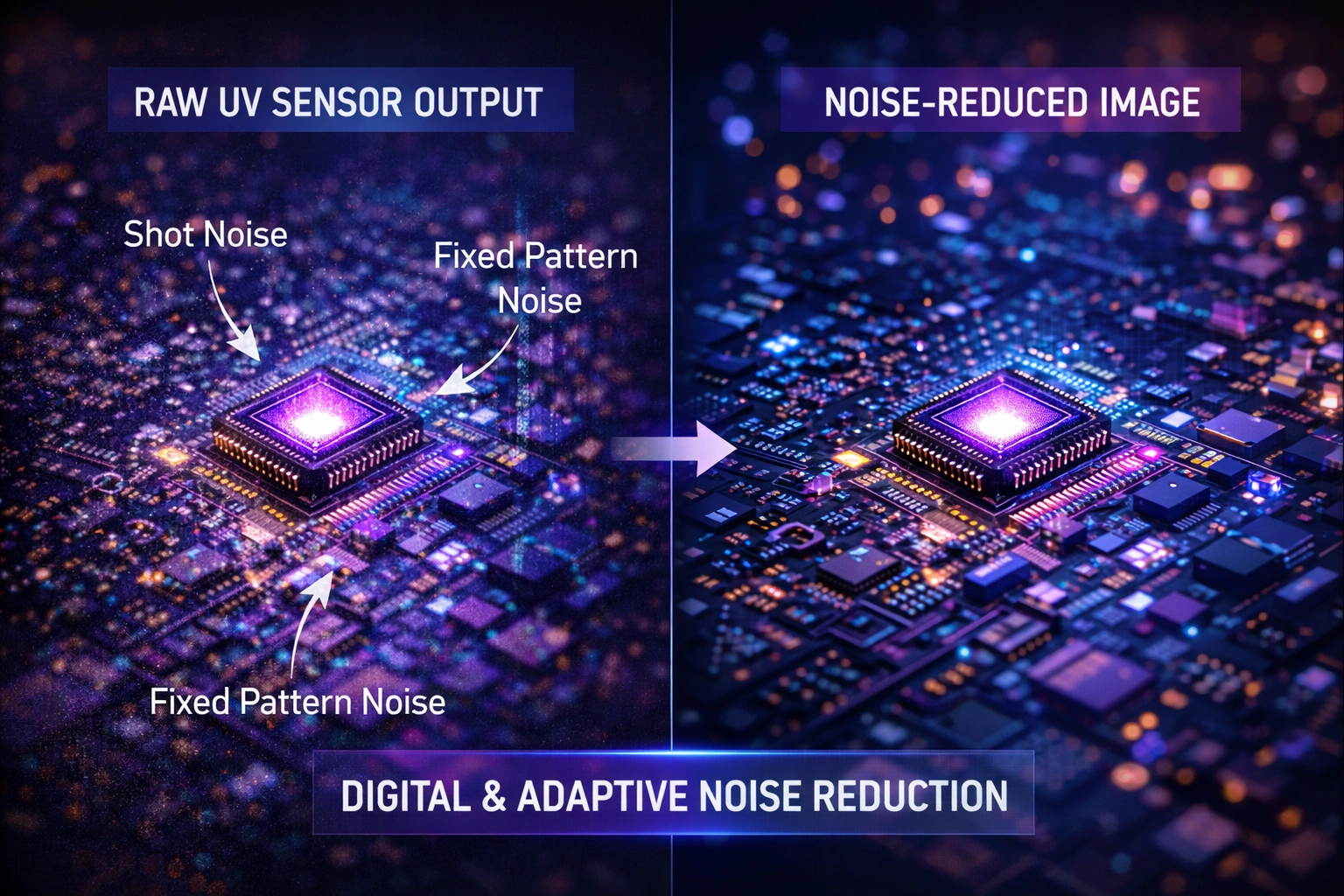
Fixed Pattern Noise (FPN)
Fixed pattern noise appears as consistent spatial variations across the sensor. These patterns remain static from frame to frame and are often caused by manufacturing imperfections, pixel response non-uniformity, or uneven amplification across sensor channels.
In UV visual systems used for precision alignment and inspection, fixed pattern noise can be especially damaging because it may be mistaken for real defects or misalignments.
Readout Noise
Readout noise is introduced during the process of converting analog sensor signals into digital data. It includes amplifier noise, quantization errors, and electronic interference from readout circuitry.
High-speed UV imaging systems are particularly vulnerable to readout noise, as faster readout rates often increase electronic instability if not carefully engineered.
Environmental and Electromagnetic Noise
External factors such as electromagnetic interference, power supply fluctuations, mechanical vibrations, and ambient radiation can also introduce noise into UV visual systems. These effects may vary depending on installation environment and system shielding quality.
Why Noise Reduction Is Critical in UV Visual Systems
Image Quality and Detail Preservation
UV imaging applications often rely on subtle contrast differences and fine surface details. Noise can obscure these details, reducing the effectiveness of visual inspection, registration accuracy, and defect detection.
Precision and Measurement Accuracy
In industrial and scientific environments, UV visual systems are frequently used for measurement tasks such as alignment verification, dimensional analysis, and surface inspection. Even small noise-induced errors can lead to incorrect measurements and costly rework.
System Reliability and Automation Stability
Automated systems depend on consistent image quality to function correctly. Excessive noise increases false positives, misclassification rates, and system instability, undermining confidence in automation.
Performance in Low-Signal Conditions
UV systems often operate at the edge of sensor sensitivity. Effective noise reduction extends usable dynamic range and improves performance under challenging lighting conditions.
Core Sensor Noise Reduction Techniques
Sensor Calibration and Characterization
Calibration is the foundation of effective noise reduction. Proper calibration allows the system to identify and compensate for predictable noise patterns.
Key calibration processes include:
Dark frame calibration to measure thermal and readout noise
Flat-field correction to remove fixed pattern noise
Gain normalization to equalize pixel response
Periodic recalibration to account for sensor aging and temperature drift
Regular calibration ensures consistent performance and prevents noise accumulation over time.
Digital Noise Reduction Algorithms
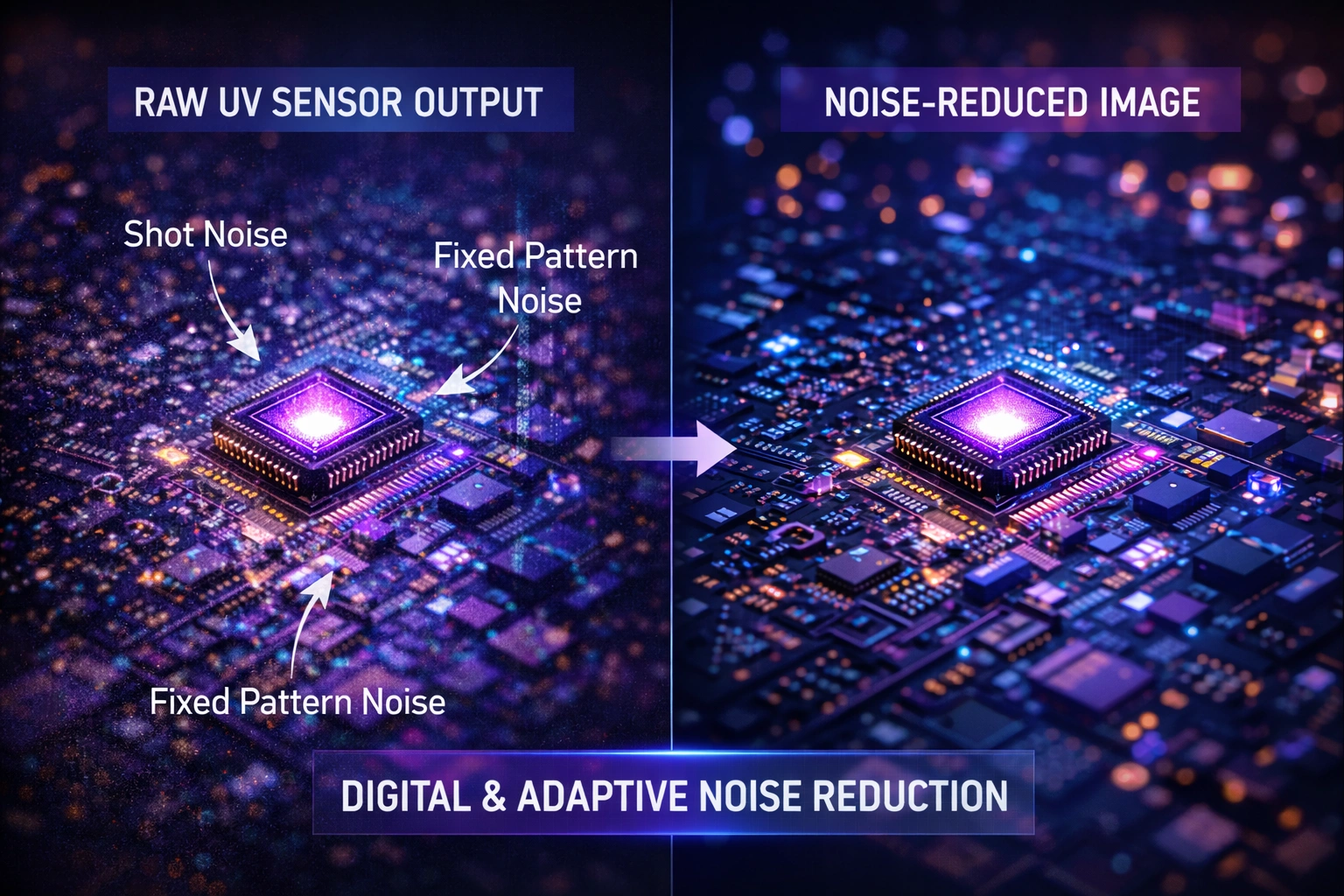
Digital noise reduction (DNR) techniques operate on captured images to identify and suppress noise while preserving useful signal information.
Spatial Filtering
Spatial filtering analyzes pixel neighborhoods within a single frame to smooth noise. Common approaches include median filtering, Gaussian smoothing, and edge-preserving filters.
Advanced spatial filters are designed to reduce noise without blurring edges, which is critical in UV inspection and printing alignment tasks.
Temporal Filtering
Temporal filtering compares multiple frames captured over time. Since noise is often random while real features remain stable, averaging across frames can significantly reduce noise.
Temporal methods are especially effective in stationary or slow-moving applications but must be carefully tuned to avoid motion blur or lag.
Adaptive Noise Reduction
Adaptive noise reduction dynamically adjusts filtering strength based on local image content and noise characteristics. Instead of applying uniform smoothing, adaptive algorithms preserve edges and fine details while aggressively reducing noise in uniform regions.
This approach is particularly valuable in UV systems where both high-contrast edges and smooth gradients must be preserved simultaneously.
Hardware-Level Improvements
High Quantum Efficiency Sensors
Sensors with higher quantum efficiency convert more incoming UV photons into usable electrical signals. This improves signal-to-noise ratio and reduces the relative impact of shot noise.
Low-Noise Amplifiers and Readout Circuits
Optimized amplifier design minimizes electronic noise during signal amplification and conversion. Modern UV sensors integrate low-noise architectures specifically engineered for high-precision imaging.
Sensor Architecture Optimization
Advanced pixel designs, improved semiconductor materials, and optimized microlenses contribute to lower intrinsic noise and improved uniformity.
Thermal Management and Cooling
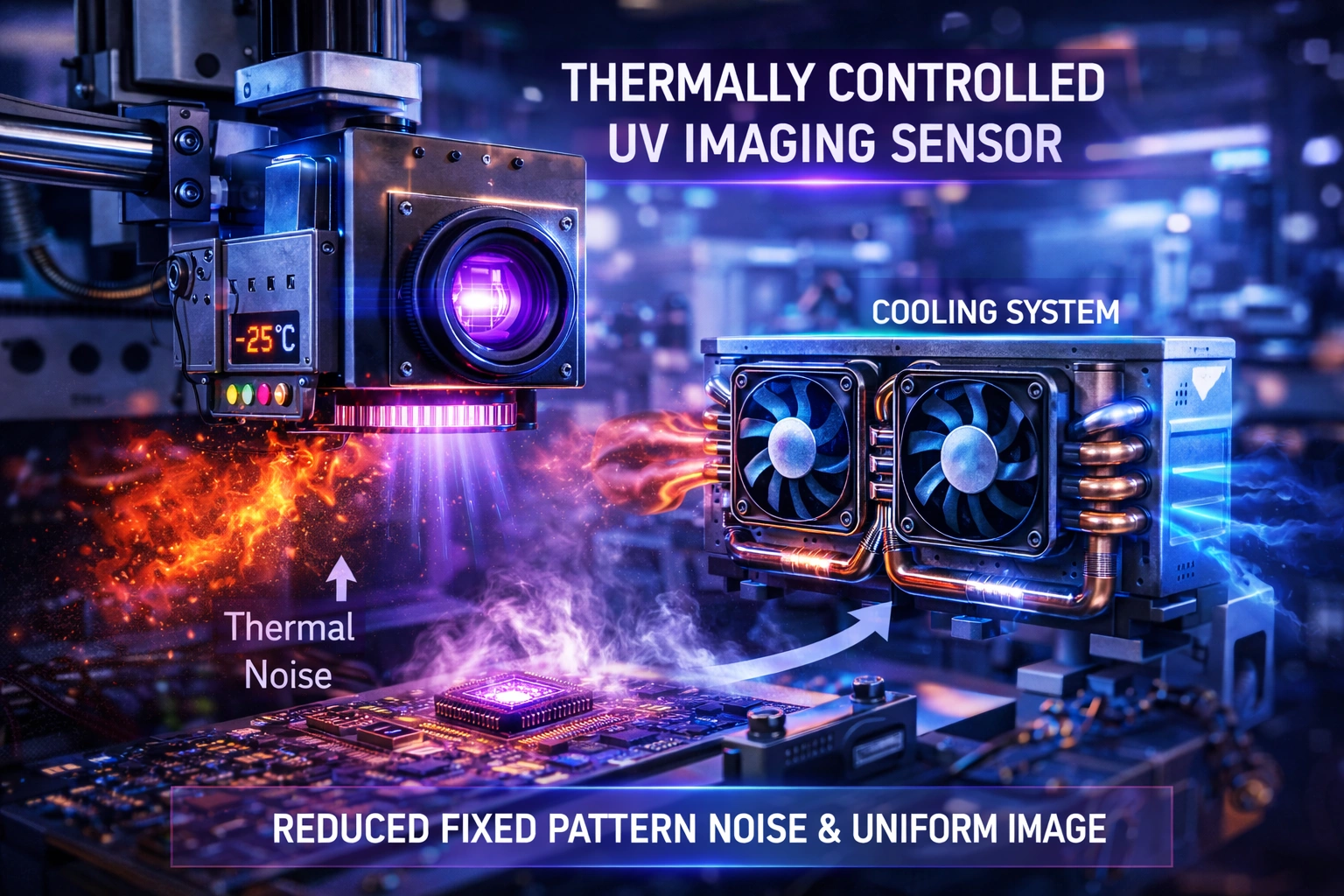
Cooling is one of the most effective ways to reduce thermal noise. Lowering sensor temperature reduces electron agitation, significantly improving image quality.
Common cooling methods include:
Passive heat sinks for moderate noise reduction
Thermoelectric cooling for precision applications
Liquid cooling for high-performance scientific systems
Proper thermal design must balance noise reduction benefits against cost, complexity, and system size constraints.
Temporal Averaging and Multi-Frame Integration
Temporal averaging combines multiple exposures of the same scene to reduce random noise. This technique is widely used in UV inspection, medical imaging, and scientific research.
Multi-frame integration improves clarity but requires stable scenes and careful synchronization to prevent artifacts.
Intelligent Exposure Control
Optimizing exposure time and gain settings helps maximize signal strength while minimizing noise amplification. Automated exposure control systems dynamically adapt to changing conditions to maintain optimal signal-to-noise ratios.
Real-World Applications of Noise Reduction
Industrial UV Printing and Inspection
In UV printing systems, noise reduction ensures accurate registration, consistent color reproduction, and reliable defect detection. Clean imaging data directly impacts print quality and production efficiency.
Medical and Biological Imaging
UV imaging plays a role in fluorescence microscopy and diagnostic analysis. Noise reduction improves contrast, enabling clearer visualization of biological structures and early disease markers.
Semiconductor and Electronics Inspection
High-resolution UV visual systems are used to inspect micro-scale features. Noise reduction is essential to avoid misinterpretation of surface defects and alignment errors.
Scientific Research and Spectroscopy
UV imaging supports advanced research applications where data accuracy is paramount. Noise reduction improves measurement repeatability and experimental reliability.
Challenges in Implementing Noise Reduction
Computational Complexity
Advanced algorithms require significant processing power, especially in real-time systems. Balancing noise reduction quality with system latency is a key engineering challenge.
Cost Constraints
High-performance sensors, cooling systems, and processing hardware increase system cost. Designers must optimize noise reduction strategies within budget limitations.
Over-Filtering Risks
Excessive noise reduction can remove fine details and reduce image sharpness. Finding the right balance between cleanliness and fidelity is essential.
Environmental Variability
Changes in temperature, lighting, and electromagnetic conditions can alter noise behavior, requiring adaptive and robust system design.
Emerging Trends in Sensor Noise Reduction
AI-Driven Noise Reduction
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to distinguish noise from signal with high accuracy. These models learn complex noise patterns and adapt dynamically to varying conditions.
Real-Time Edge Processing
Noise reduction is moving closer to the sensor through on-chip processing and edge computing. This reduces latency and improves system responsiveness.
Smarter Sensor Materials
New materials and sensor designs promise lower intrinsic noise and improved UV sensitivity, reducing the need for aggressive post-processing.
Integrated System Optimization
Future UV visual systems will combine hardware, firmware, and software noise reduction into unified, self-optimizing platforms.
Best Practices for Optimizing Noise Reduction
Perform regular sensor calibration
Control operating temperature consistently
Use adaptive rather than aggressive filtering
Optimize exposure and gain settings
Combine hardware and software strategies
Monitor noise performance over system lifespan
Conclusion
Sensor noise reduction is a cornerstone of high-performance UV visual systems. As applications demand greater precision, reliability, and automation, noise management becomes increasingly critical. Effective noise reduction requires a balanced approach that integrates sensor design, calibration, signal processing, thermal control, and intelligent software.
By understanding noise sources and applying the right combination of techniques, organizations can significantly enhance image quality, improve system stability, and unlock the full potential of UV visual technology. As advancements in AI, sensor materials, and real-time processing continue, the future of noise-free UV imaging looks more promising than ever.
You can explore our high-quality Visual Positioning UV printers here, which incorporate advanced noise reduction techniques to enhance your imaging capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is sensor noise in UV visual systems?
Sensor noise refers to unwanted signal variations that distort or obscure true image data captured by UV sensors.
Why is noise more challenging in UV imaging?
UV imaging often operates in low-signal conditions, making noise more visible and impactful than in visible-light systems.
Can sensor noise be completely eliminated?
No, but it can be significantly reduced through calibration, hardware optimization, cooling, and intelligent processing.
Do noise reduction techniques affect image sharpness?
If applied incorrectly, yes. Properly tuned techniques preserve detail while minimizing noise.
What is the future of noise reduction in UV systems?
AI-driven algorithms, smarter sensors, and integrated edge processing will define the next generation of noise reduction solutions
