How to Reduce Static Electricity Problems in UV Printing

Static electricity is one of the most overlooked yet disruptive challenges in modern UV printing environments. While UV printing technology is known for its speed, durability, and versatility across a wide range of substrates, uncontrolled static charge can quietly undermine print quality, slow down production, and increase material waste. From ink misting and substrate misalignment to dust attraction and curing inconsistencies, static electricity affects nearly every stage of the UV printing process.
As UV printers operate at high speeds and interact with non-porous materials such as acrylic, PVC, PET, foam board, and coated papers, the likelihood of static charge buildup increases significantly. Many print operators focus on ink, curing lamps, and print heads but fail to recognize static electricity as a root cause behind recurring print defects and machine inefficiencies.
This article provides a comprehensive, practical, and industry-tested guide to understanding static electricity in UV printing and, more importantly, how to control and reduce it effectively. Whether you run a small print shop or a large industrial UV printing setup, the strategies outlined here will help you improve print consistency, protect equipment, and enhance overall productivity.
Understanding Static Electricity in UV Printing
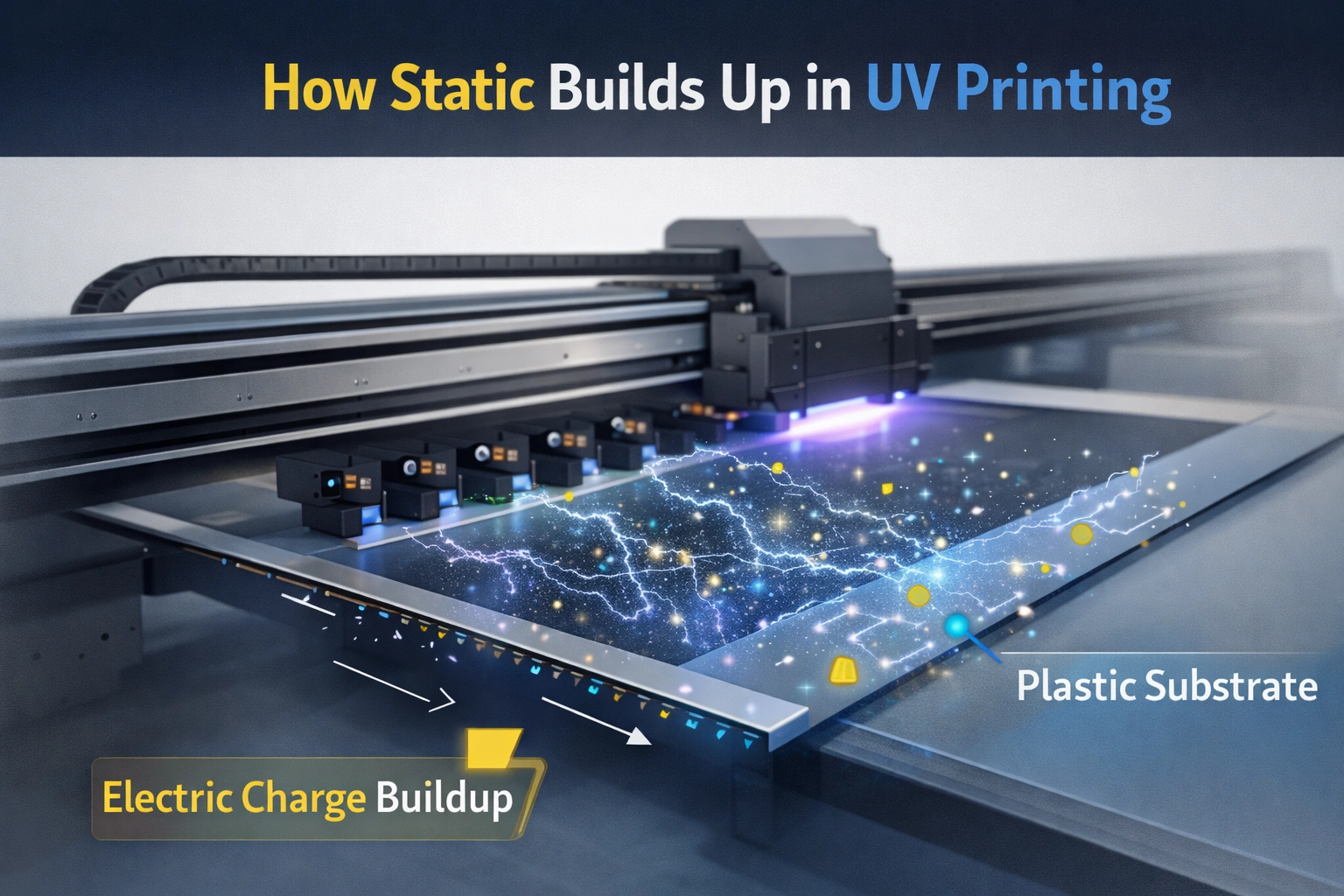
Static electricity occurs when there is an imbalance of electrical charges on the surface of a material. In UV printing, this imbalance is commonly generated when substrates move rapidly through rollers, feeders, conveyors, or vacuum tables. Friction, separation, and environmental conditions all contribute to the accumulation of static charge.
Unlike traditional printing processes, UV printing often involves non-absorbent and synthetic substrates that do not naturally dissipate electrical charge. As a result, static electricity remains trapped on the surface, interfering with ink behavior and substrate handling.
Understanding how static is generated and how it behaves is the first step toward controlling it.
Primary Sources of Static Electricity in UV Printing
1. Environmental Conditions
Low humidity is the single biggest contributor to static buildup in printing environments. Dry air acts as an insulator, preventing electrical charges from dissipating naturally. This is especially common in air-conditioned rooms or during winter months.
2. Substrate Characteristics
Different materials generate static at different levels:
Plastics like PVC, PET, and acrylic generate high static
Coated papers and synthetic films hold charge longer
Lightweight flexible media is more prone to static attraction
3. Mechanical Movement
High-speed feeding, friction between rollers, vacuum suction, and rapid material separation all contribute to static generation. The faster the substrate moves, the higher the static potential.
4. UV Ink and Curing Interaction
UV inks and curing lamps can intensify static effects by altering surface tension and electrical behavior on substrates, especially during rapid curing cycles.
Negative Impact of Static Electricity on UV Printing
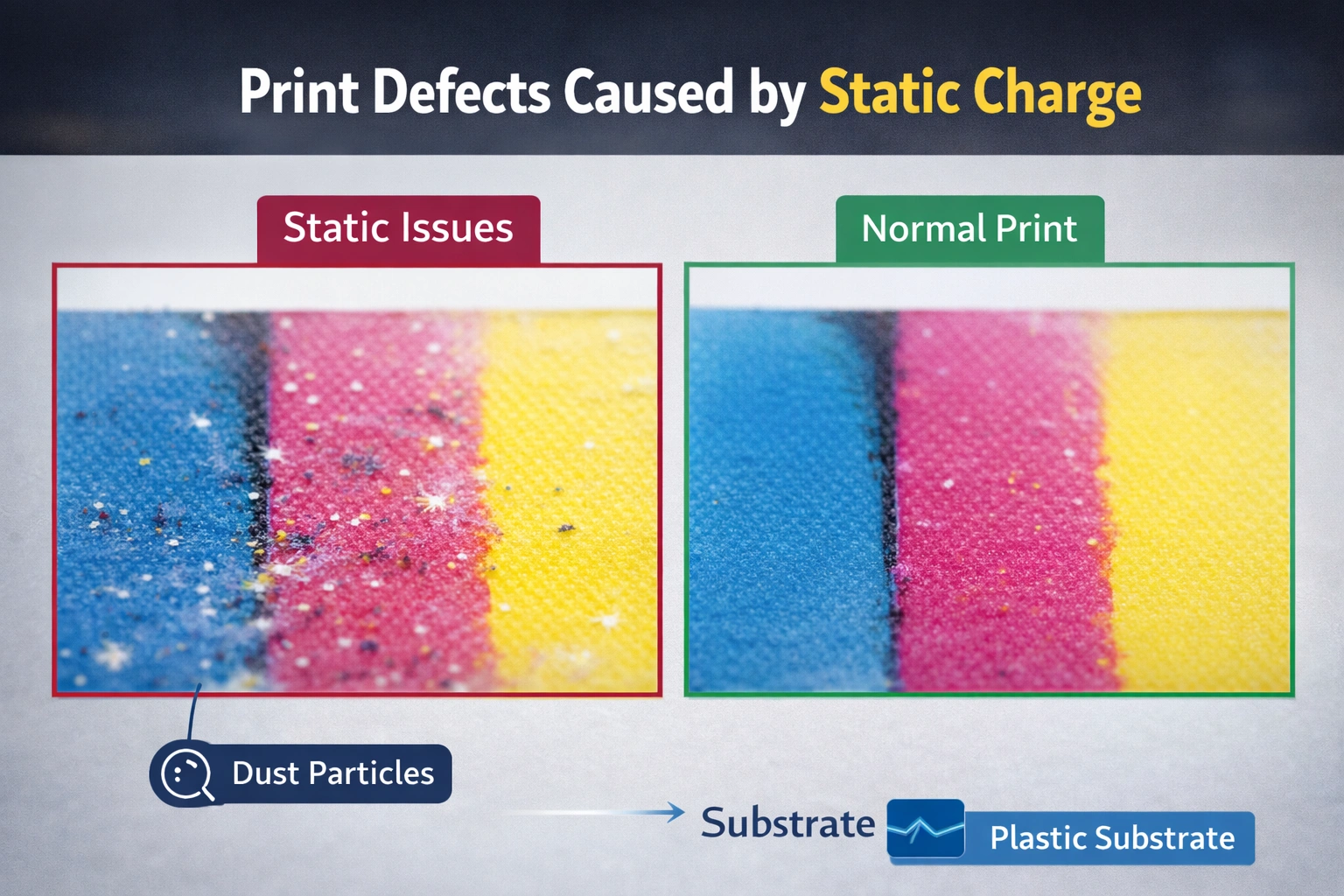
1. Reduced Print Quality
Static electricity attracts airborne dust, fibers, and particles directly onto the print surface. These contaminants become permanently cured into the ink, resulting in pinholes, bumps, and surface defects.
2. Ink Misting and Overspray
Static charge can cause ink droplets to repel or scatter instead of landing accurately, leading to fuzzy edges, color inconsistency, and reduced sharpness.
3. Poor Ink Adhesion
Electrostatic interference disrupts ink wetting and curing, causing weak adhesion, cracking, or peeling—especially on plastics and coated materials.
4. Media Feeding Errors
Static can cause sheets to stick together, misfeed, skew, or lift during printing, leading to registration issues and machine stoppages.
5. Equipment Stress and Downtime
Uncontrolled static increases wear on rollers, sensors, and transport systems, raising maintenance costs and increasing downtime.
Effective Strategies to Reduce Static Electricity in UV Printing

1. Maintain Optimal Humidity Levels
Humidity control is the foundation of static management.
Recommended humidity range: 40%–60% relative humidity
Best practices:
Install industrial humidifiers in print rooms
Use digital hygrometers to monitor levels continuously
Avoid extreme temperature fluctuations
Maintain stable airflow without over-drying the environment
Consistent humidity allows electrical charges to dissipate naturally, reducing static at the source.
2. Use Ionization Technology
Ionizers are one of the most effective tools for neutralizing static electricity in UV printing.
Common ionization solutions include:
Ionizing bars
Ionizing air blowers
Anti-static nozzles
These devices emit positive and negative ions that neutralize surface charges on substrates before, during, or after printing.
Placement tips:
Install ionizers near feed tables and print heads
Use ionizers before UV curing zones
Ensure regular cleaning for optimal performance
3. Select Low-Static Printing Materials
Material selection plays a critical role in static control.
Tips for substrate selection:
Choose UV-compatible materials with anti-static coatings
Avoid excessively lightweight or thin media where possible
Test new substrates before full production runs
Store materials in controlled environments
Many suppliers offer static-dissipative substrates specifically designed for UV printing applications.
4. Proper Equipment Grounding
Grounding allows electrical charges to safely discharge from machines and substrates.
Grounding best practices:
Ensure all UV printers are properly grounded
Ground feed tables, conveyors, and finishing equipment
Regularly inspect grounding wires and connectors
Remove corrosion or loose connections immediately
Improper grounding can amplify static problems rather than reduce them.
5. Implement Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Dust buildup increases static attraction and contamination.
Maintenance checklist:
Clean rollers, belts, and vacuum tables regularly
Remove ink residue and dust from machine surfaces
Inspect transport systems for friction points
Replace worn rollers and belts
A clean machine environment reduces both static generation and its negative effects.
6. Optimize Printing Speed and Pressure
High speeds and excessive pressure increase friction and static charge.
Optimization tips:
Reduce printing speed when working with high-static substrates
Adjust vacuum strength carefully
Balance print head height and pressure
Avoid unnecessary substrate bending or flexing
Fine-tuning machine parameters can dramatically reduce static buildup.
7. Use Anti-Static Solutions and Coatings
Anti-static sprays, wipes, and coatings can help neutralize static on substrates before printing.
Usage tips:
Use solutions approved for UV printing
Apply evenly and allow proper drying time
Avoid over-application that could affect ink adhesion
These solutions are especially helpful for short-run jobs or specialty materials.
Advanced Static Control Techniques for High-Volume UV Printing
1. Climate-Controlled Print Rooms
Professional UV printing facilities benefit greatly from dedicated climate-controlled environments that maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels year-round.
2. Static Monitoring Systems
Advanced operations use static meters to measure charge levels on substrates in real time, hooking data into quality control workflows.
3. Integrated Anti-Static Automation
Modern UV printers increasingly integrate ionization and grounding directly into the machine design, reducing manual intervention.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring humidity levels
Relying on one solution instead of a combined approach
Skipping regular maintenance
Using incompatible anti-static products
Overlooking grounding during installation
Avoiding these mistakes ensures long-term static control rather than temporary fixes.
Conclusion
Static electricity is an invisible but powerful force that can severely impact UV printing performance if left unmanaged. From print defects and ink adhesion issues to media handling errors and equipment stress, static problems affect both quality and profitability.
The good news is that static electricity is highly controllable with the right combination of environmental management, equipment upgrades, material selection, and operational discipline. By maintaining optimal humidity, using ionization technology, grounding equipment properly, and adopting smart printing practices, UV print operators can significantly reduce static-related issues.
As UV printing technology continues to advance, proactive static management will remain a critical factor in achieving consistent, high-quality results and maintaining a competitive edge in the printing industry.explore our high-quality UV printers here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is static electricity in UV printing?
Static electricity is an imbalance of electrical charges on substrates that can attract dust, disrupt ink placement, and cause mechanical issues during UV printing.
Why does low humidity increase static problems?
Dry air prevents electrical charges from dissipating, allowing static to build up more easily on printing materials.
Are ionizers necessary for UV printing?
For high-speed or plastic-based UV printing, ionizers are highly recommended as they neutralize static effectively.
Can static electricity damage UV printers?
Yes, prolonged static exposure can stress sensors, rollers, and electronic components, increasing maintenance costs.
How often should static control systems be checked?
Humidity, grounding, and ionization systems should be monitored daily and inspected as part of routine maintenance schedules.

